3459 - Length of Longest V-Shaped Diagonal Segment
info
- 문제 보기: 3459 - Length of Longest V-Shaped Diagonal Segment
- 소요 시간: 47분 29초
- 풀이 언어:
java - 체감 난이도: 3️⃣~4️⃣ (3.7)
- 리뷰 횟수: ✅
풀이 키워드
스포주의
DP
풀이 코드
info
- 메모리: 143900 KB
- 시간: 424 ms
class Solution {
int[] dy = {-1, -1, 1, 1}; // lu, ru, rd, ld
int[] dx = {-1, 1, 1, -1};
int[][] grid;
int n, m;
int[][][][] memo;
int dp(int y, int x, int dir, int turned) {
//System.out.println("dp(" + y + ", " + x + ", " + dir + ", " + turned + ")");
if ((y == 0 || y == n-1 || x == 0 || x == m-1) && turned == 1) return 1;
if (memo[y][x][dir][turned] != 0) return memo[y][x][dir][turned];
int res = 0;
int curVal = grid[y][x];
// no turn
{
int ny = y + dy[dir];
int nx = x + dx[dir];
// bound check
if (0 <= ny && ny <= n-1 && 0 <= nx && nx <= m-1) {
int nxtVal = grid[ny][nx];
// value check
if (nxtVal != 1 && nxtVal != curVal)
res = Math.max(res, dp(ny, nx, dir, turned));
}
}
// turn
if (turned == 0) {
int nTurned = 1; // true
int ndir = (dir + 1) % 4;
int ny = y + dy[ndir];
int nx = x + dx[ndir];
// bound check
if (0 <= ny && ny <= n-1 && 0 <= nx && nx <= m-1) {
int nxtVal = grid[ny][nx];
// value check
if (nxtVal != 1 && nxtVal != curVal)
res = Math.max(res, dp(ny, nx, ndir, nTurned));
}
}
//System.out.println("dp(" + y + ", " + x + ", " + dir + ", " + turned + ") = " + (res+1));
return memo[y][x][dir][turned] = res + 1;
}
public int lenOfVDiagonal(int[][] grid) {
this.grid = grid;
n = grid.length;
m = grid[0].length;
memo = new int[n][m][4][2];
int mx = 0;
int self = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; ++j) {
if (grid[i][j] != 1) continue;
self = 1; // 1 exists
for (int d = 0; d < 4; ++d) { // 4 directions
int ny = i + dy[d];
int nx = j + dx[d];
// bound check
if (0 <= ny && ny <= n-1 && 0 <= nx && nx <= m-1) {
// if matches the first number of the seq
if (grid[ny][nx] == 2)
mx = Math.max(mx, dp(ny, nx, d, 0));
}
}
}
}
return mx == 0 ? self : mx+1;
}
}
풀이 해설
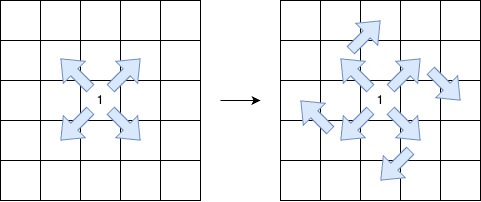
첫 칸은 1, 이후부턴 2, 0, 2, 0, ... 식으로 이어지며
진행방향은 대각선만 가능하고, 최대 딱 1번 시계방향 90도로 진행방향을 꺾을 수 있을 때
가장 길게 뽑을 수 있는 경로의 길이를 구하는 고차원 DP 문제이다.
🥲 실수 그마안~
처음엔 turn할 경우의 로직을 이렇게 설정했었고
구버전 turn 로직
// turn
if (turned == 0) {
int nTurned = 1; // true
int ndir = (dir + 1) % 4;
int ny = y + dy[ndir];
int nx = x + dx[ndir];
...
driver 단에선 초기 dp를 이렇게 호출하는 실수를 했다.
구버전 driver 로직
// if matches the first number of the seq
if (grid[ny][nx] == 2)
mx = Math.max(mx, dp(i, j, d, 0));
즉, dp 첫 호출을 1이 쓰인 칸으로 넘겨버린 것이다.
그래서 return 단도 이러했다. (mx는 '1' 칸까지 합산된 값)
구버전 return 로직
return mx == 0 ? self : mx;
구버전 코드와 전체 비교
🔐 이 콘텐츠는 암호화되어 있습니다.
하지만 이는 다음의 케이스에서 얄짤없이 WA 걸렸는데
input
[[2,0,2,0,2,0],
[0,1,2,2,2,0],
[2,0,1,0,2,0],
[2,0,0,0,1,0],
[0,0,2,0,2,0],
[2,0,2,0,2,0],
[2,0,2,0,2,0],
[2,0,0,0,2,0]]
이게 왜 틀렸냐고? 디버깅을 해보자.
상단의 풀이 코드에서 해당 구버전 로직으로 수정 후, 주석 떼고 출력해보면 다음과 같다. (가독성을 위해 줄바꿈 넣음)
stdout
dp(1, 1, 0, 0)
dp(0, 0, 0, 0)
dp(0, 0, 0, 0) = 1
dp(0, 2, 1, 1)
...
여기서 dp(0, 2, 1, 1)이 출력되었다는 점에서 조건이 잘못됨을 알 수 있다.
왜냐하면 (1, 1)은 시작점인데, 바로 다음 진행 칸인 (0, 2)에서 turned가 1(true) 일 수 없기 때문이다.
이는 방금 전 언급한, 하단의 라인에서 조건이 잘못되었기 때문이다.
// turn
if (turned == 0) {
int nTurned = 1; // true
int ndir = (dir + 1) % 4;
int ny = y + dy[ndir];
int nx = x + dx[ndir];
...
여기서 turned == 0 뿐만 아니라 curVal != 1 이라는 조건까지 추가되어야 AC를 받을 수 있다.
하지만 근본적으로는 driver 단에서 첫 dp 호출을 i, j로 넘겨버린 것이 원인이기 때문에,
최종 풀이코드는 다음의 3가지 수정을 거쳐 AC를 받았다.
- 첫 dp를
ny,nx로 넘김 - dp 내에서 조건을
turned == 0만 사용 - 최종 return 문에선
mx에 '1'칸이 합산되어있지 않으니mx+1을 반환
메모
- I ❤️ DP
- 그림만 보고 삼성st 빡구현인줄 알았는데 낚였다. 🎣
- GPT-5 mini thinking 모드에서 디버깅 못하고 뺑이치길래 답답해서 내가 함...