정보처리기사 실기 프로그래밍 문제 유형
이 글에서는 개정된 정보처리기사 실기 시험의 프로그래밍 문제 유형에 대해서 다룬다.
프로그래밍 문제는 전공자 비전공자 할 것 없이, 해당 언어를 좀 써봤��으면 하루 벼락치기도 가능한 수준이다.
언어에 익숙하다면 거저 주는 문제인데 10문제 가량 되므로, 나오지도 않을 개념 달달 외우는 불상사가 없도록 하자.
들어가기에 앞서..
🕗️ 벼락치기러를 위한 정상화 타임 존재
9시에 시험 시작하는줄 알았는데 9시까지 입실이고
9시부터 9시 30분까지 방송을 핑계로 벼락치기러들 기억을 포맷시키는 정상화 타임이 존재한다.
🦓 검은건 코드요 흰건 종이로다
흑백 인쇄이므로 코드에 prettify 따윈 되어있지 않고, 라인 넘버도 없다.
그리고 파이썬 제외 Java 등에선 indent를 정확히 안지킨다.
public static void main(String[] args) {
코드가
이렇게
써있어요
}
공통
📌 재귀함수
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] data = {3, 5, 8, 12, 17};
System.out.println(func(data, 0, data.length - 1));
}
static int func(int[] a, int st, int end) {
if (st >= end) return 0;
int mid = (st + end) / 2;
return a[mid] + Math.max(func(a, st, mid), func(a, mid + 1, end));
}
}
class Node:
def __init__(self, value):
self.value = value
self.children = []
def tree(li):
nodes = [Node(i) for i in li]
for i in range(1, len(li)):
nodes[(i - 1) // 2].children.append(nodes[i])
return nodes[0]
def calc(node, level=0):
if node is None:
return 0
return (node.value if level % 2 == 1 else 0) + sum(calc(n, level + 1) for n in node.children)
li = [3, 5, 8, 12, 15, 18, 21]
root = tree(li)
print(calc(root))
#include
int f(int n) {
if(n<=1) return 1;
else return n*f(n-1);
}
int main() {
printf("%d", f(7));
}
📌 switch - case 낚시
#include <stdio.h>
void main(){
int n[3] = {73, 95, 82};
int sum = 0;
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
sum += n[i];
}
switch(sum/30){
case 10:
case 9: printf("A");
case 8: printf("B");
case 7:
case 6: printf("C");
default: printf("D");
}
}
Java
정처기에서 제일 현웃인건 자바 파트이다. 수험생을 어떻게든 틀리게 하려는 출제진의 눈물나는 노력이 느껴진다.
대체 어디서 다들 알아온건지 모를, 실무에서 쓸 리 없는 각종 안티패턴을 들고 온다.
객체지향 언어답게 상속 문제 위주로 출제된다.
📌 스텔스 super
상속 관계에서 자식 클래스의 생성자에 super()가 명시되어있지 않으면
컴파일러가 자동으로 super()를 첫 줄에 삽입하는데, 이를 알고있는지 묻는 유형이다.
📌 업캐스팅
거의 무조건적으로 출제되는 유형.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Child();
System.out.println(Parent.total);
}
}
class Parent {
static int total = 0;
int v = 1;
public Parent() {
total += (++v);
show();
}
public void show() {
total += total;
}
}
class Child extends Parent {
int v = 10;
public Child() {
v += 2;
total += v++;
show();
}
@Override
public void show() {
total += total * 2;
}
}
public class main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
A b = new B();
b.paint();
b.draw();
}
}
class A {
public void paint() {
System.out.print("A");
draw();
}
public void draw() {
System.out.print("B");
draw();
}
}
class B extends A {
public void paint() {
super.draw();
System.out.print("C");
this.draw();
}
public void draw() {
System.out.print("D");
}
}
📌 업캐스팅과 멤버변수
이 또한 업캐스팅 관련 문제인데,
메소드는 실 객체를 기준으로 하는 반면 멤버변수는 참조 타입 기준임을 알아야 하는 문제이다.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Base a = new Derivate();
Derivate b = new Derivate();
System.out.print(a.getX() + a.x + b.getX() + b.x);
}
}
class Base {
int x = 3;
int getX() {
return x * 2;
}
}
class Derivate extends Base {
int x = 7;
int getX() {
return x * 3;
}
}
📌 static 메소드와 동적바인딩
static 메소드는 동적바인딩이 적용되지 않는 점을 이용해서 낚시를 시도한다.
public class Main{
public static class Parent {
public int x(int i) { return i + 2; }
public static String id() { return "P";}
}
public static class Child extends Parent {
public int x(int i) { return i + 3; }
public String x(String s) { return s + "R"; }
public static String id() { return "C"; }
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Parent ref = new Child();
System.out.println(ref.x(2) + ref.id());
}
}
📌 call by value를 아십니까?
public class Main {
public static void change(String[] data, String s){
data[0] = s;
s = "Z";
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String data[] = { "A" };
String s = "B";
change(data, s);
System.out.print(data[0] + s);
}
}
📌 문자열 비교
레퍼런스 비교인지 값 비교인지 구분할 수 있어야 하며,
String Constant Pool과 같은 다소 지엽적인 interning 관련 내용을 출제하기도 한다.
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = 'Programming';
String str2 = 'Programming';
String str3 = new String('Programming');
println(str1==str2)
println(str1==str3)
println(str1.equals(str3))
print(str2.equals(str3))
}
}
📌 Type Erasure 낚시
자바의 오버로딩이 정적 바인딩인 점을 이용하여 제네릭 Type Erasure 관련 낚시 문제를 출제한 적 있다.
자격증 문제 치고는 지엽적인 편이다.
class Main {
public static class Collection<T> {
T value;
public Collection(T t) {
value = t;
}
public void print() {
new Printer().print(value);
}
class Printer {
void print(Integer a){
System.out.print("A" + a);
}
void print(Object a){
System.out.print("B" + a);
}
void print(Number a){
System.out.print("C" + a);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Collection<>(0).print();
}
}
📌 함수형 프로그래밍과 람다
public class Main {
static interface F {
int app(int x) throws Exception;
}
public static int run(F f) {
try {
return f.app(3);
} catch (Exception e) {
return 7;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
F f = (x) -> {
if (x > 2) {
throw new Exception();
}
return x * 2;
};
System.out.print(run(f) + run((int n) -> n + 9));
}
}
📌 try - catch - finally
문법만 알고 있으면 되는 거저 주는 문제이다.
📌 Exception
일반적인 Exception들에 대하여 묻는다.
try - catch 구문과 같이 응용해서 출제되는 경우가 많다.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 5, b = 0;
try {
System.out.print(a/b);
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.print("출력1");
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.print("출력2");
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.print("출력3");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.print("출력4");
} finally {
System.out.print("출력5");
}
}
}
public class ExceptionHandling {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum = 0;
try {
func();
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
sum = sum + 1;
} catch (Exception e) {
sum = sum + 10;
} finally {
sum = sum + 100;
}
System.out.print(sum);
}
static void func() throws Exception {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
}
📌 split
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "ITISTESTSTRING";
String[] result = str.split("T");
System.out.print(result[3]);
}
}
C
C언어는 포인터로 평소 실험 좀 해봤으면 Java 문제보다 쉬울 것이다.
Java는 고의적인, 정처기에서만 볼 것 같은 문제로 오답을 유도하기 때문에 자바맨도 강제로 기출을 보게 하지만,
C언어는 출제 포커스가 함정보단 '포인터로 기죽이기'에 가깝기 때문이다.
📌 포인터와 배열
구조체 포인터와 섞어서 출제하기도 한다.
#include <stdio.h>
struct data {
int x;
int y;
};
int main() {
struct data a[] = {{1, 2}, {3, 4}, {5, 6}};
struct data *ptr = a;
struct data **pptr = &ptr;
(*pptr)[1] = (*pptr)[2];
printf("%d 그리고 %d", a[1].x, a[1].y);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int arr[3][3] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};
int* parr[2] = {arr[1], arr[2]};
printf("%d", parr[1][1] + *(parr[1]+2) + **parr);
return 0;
}
📌 연결리스트
연결리스트를 생성하고 순서를 재배열해서 출력시키면 어떻게 나올지 묻는 유형이 많다.
전공자들은 연결리스트 구현을 한번쯤 다 해보기 때문에 거저 주는 문제가 된�다.
괜히 꼬아보겠다고 구조체 변수 네이밍을 비직관적으로 만들어놓기도 한다.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct Data {
int value;
struct Data *next;
} Data;
Data* insert(Data* head, int value) {
Data* new_node = (Data*)malloc(sizeof(Data));
new_node->value = value;
new_node->next = head;
return new_node;
}
Data* reconnect(Data* head, int value) {
if (head == NULL || head->value == value) return head;
Data *prev = NULL, *curr = head;
while (curr != NULL && curr->value != value) {
prev = curr;
curr = curr->next;
}
if (curr != NULL && prev != NULL) {
prev->next = curr->next;
curr->next = head;
head = curr;
}
return head;
}
int main() {
Data *head = NULL, *curr;
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++)
head = insert(head, i);
head = reconnect(head, 3);
for (curr = head; curr != NULL; curr = curr->next)
printf("%d", curr->value);
return 0;
}
📌 자료구조 구현체
이것도 포인터의 현 상태만 잘 시각화해서 실수하지 않고 상태 추적하면 풀리는 문제이기에 어렵지 않다.
스택, 큐, 환형 큐 등이 출제될 수 있다.
#include <stdio.h>
#define SIZE 3
typedef struct {
int a[SIZE];
int front;
int rear;
} Queue;
void enq(Queue* q, int val){
q->a[q->rear] = val;
q->rear = (q->rear + 1) % SIZE;
}
int deq(Queue* q) {
int val = q->a[q->front];
q->front = (q->front + 1) % SIZE;
return val;
}
int main() {
Queue q = {{0}, 0, 0};
enq(&q,1); enq(&q,2); deq(&q); enq(&q, 3);
int first = deq(&q);
int second = deq(&q);
printf("%d 그리고 %d", first, second);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 10
int isWhat[MAX_SIZE];
int point= -1;
int isEmpty() {
if (point == -1) return 1;
return 0;
}
int isFull() {
if (point == 10) return 1;
return 0;
}
void into(int num) {
if (point >= 10) printf("Full");
else isWhat[++point] = num;
}
int take() {
if (isEmpty() == 1) printf("Empty");
else return isWhat[point--];
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[]){
int e;
into(5); into(2);
while(!isEmpty()){
printf("%d", take());
into(4); into(1); printf("%d", take());
into(3); printf("%d", take()); printf("%d", take());
into(6); printf("%d", take()); printf("%d", take());
}
return 0;
}
📌 비트 연산
비트 연산자를 안다면 계산 실수만 안하면 된다.
0xA8 같은 8비트 값을 2진수로 변환해서 직접 비트 연산할 수 있어야 한다.
#include <stdio.h>
typedef struct student {
char* name;
int score[3];
} Student;
int dec(int enc) {
return enc & 0xA5;
}
int sum(Student* p) {
return dec(p->score[0]) + dec(p->score[1]) + dec(p->score[2]);
}
int main() {
Student s[2] = { "Kim", {0xA0, 0xA5, 0xDB}, "Lee", {0xA0, 0xED, 0x81} };
Student* p = s;
int result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
result += sum(&s[i]);
}
printf("%d", result);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int v1 = 0, v2 = 35, v3 = 29;
if (v1 > v2 ? v2 : v1) {
v2 = v2 << 2;
} else {
v3 = v3 << 2;
}
printf("%d", v2+v3);
}
📌 call by value를 아십니까?
#include <stdio.h>
void swap(int a, int b) {
int t = a;
a = b;
b = t;
}
int main() {
int a = 11;
int b = 19;
swap(a, b);
switch(a) {
case 1:
b += 1;
case 11:
b += 2;
default:
b += 3;
break;
}
printf("%d", a-b);
}
Python
📌 리스트 슬라이싱
리스트 슬라이싱은 파이썬의 꽃이라서 거저 주는 문제이다.
def func(lst):
for i in range(len(lst) //2):
lst[i], lst[-i-1] = lst[-i-1], lst[i]
lst = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
func(lst)
print(sum(lst[::2]) - sum(lst[1::2]))
📌 split
파이썬�으로 코테를 풀어봤다면 split은 써볼수밖에 없기 때문에, 거저 주는 문제이다.
print("파이썬 입출력에 대한 문제입니다.")
num1, num2 = input()._____()
num1 = int(num1)
num2 = int(num2)
print(num1,num2)
num3 = num1 + num2
print(num1 + " + " + num2 + " = " + num3)
📌 f-string
어려운 문법은 아니나 약간 지엽적인 느낌이 없잖아 있긴 함.
def fnCalculation(x,y):
result = 0;
for i in range(len(x)):
temp = x[i:i+len(y)]
if temp == y:
result += 1;
return result
a = "abdcabcabca"
p1 = "ab";
p2 = "ca";
out = f"ab{fnCalculation(a,p1)}ca{fnCalculation(a,p2)}"
print(out)
📌 dictionary
기본 연산과 key - value 구조 알면 다 풀리는 문제이다. 거저 주는 문제.
lst = [1,2,3]
dst = {i : i * 2 for i in lst}
s = set(dst.values())
lst[0] = 99
dst[2] = 7
s.add(99)
print(len(s & set(dst.values())))
📌 set
기본 연산과 집합의 특성, 교집합 차집합 이런거 알면 다 풀리는 문제이다. 거저 주는 문제.
a = {'한국', '중국', '일본'}
a.add('베트남')
a.add('중국')
a.remove('일본')
a.update({'홍콩', '한국', '태국'})
print(a)
SQL
기본적인 문법만 나오고 지엽적인건 없으니 차라리 관계대수 기호랑 DB 이론을 더 보는 것이 낫다.
📌 SELECT - FROM - WHERE
📌 JOIN - ON
📌 GROUP BY - HAVING
📌 ORDER BY
📌 INSERT INTO - VALUES
2023년도 2회차 참고
📌 CASCADE, RESTRICT
📌 집합 연산
UNION, INTERSECT 등
📌 집계 함수
MIN, MAX, SUM, AVG, COUNT
📌 다중 조건
AND, OR, IN
📌 서브 쿼리
SELECT
count(*)
FROM employee AS e JOIN project AS p ON e.project_id = p.project_id
WHERE p.name IN (
SELECT name FROM project p WHERE p.project_id IN (
SELECT project_id FROM employee GROUP BY project_id HAVING count(*) < 2
)
);
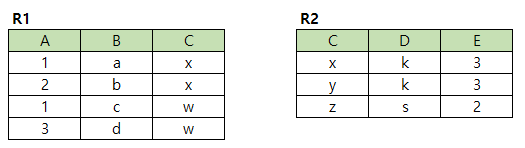
SELECT
B
FROM
R1
WHERE
C IN (SELECT C FROM R2 WHERE D="k");